Despite promising reform and introducing a new constitution in 2011, Morocco’s treatment of dissidents indicates the changes were just window dressing.
Despite promising reform and introducing a new constitution in 2011, Morocco’s treatment of dissidents indicates the changes were just window dressing, Samia Errazzouki writes.
Morocco’s King Mohammed VI announced a constitutional reform process during a 9 March 2011 speech, following popular protests organised by the 20 February Movement. Regime supporters and allies — France and the United States — hailed the move towards reform as “unprecedented.” Morocco was soon referred to as the “model for the region.”
But the government’s repression of freedom of expression has remained steadfast even after the new constitution.
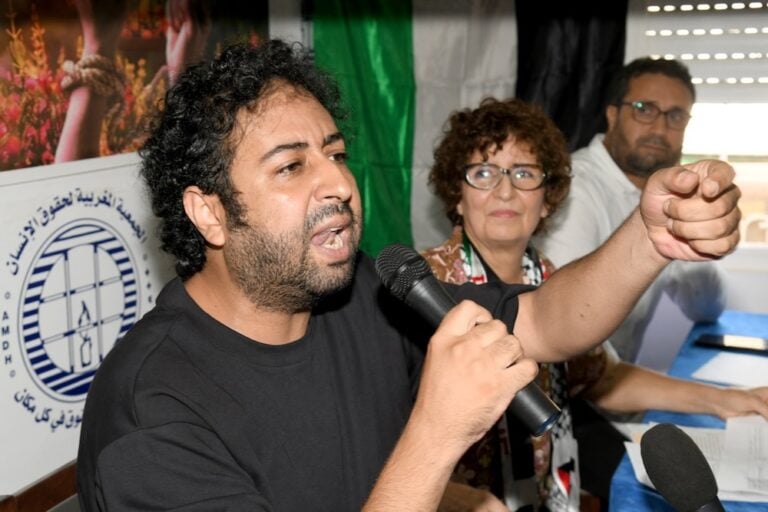
Most recently, in March 2013 dissident rapper Mouad Belghouat (alias El Haqed) was released from jail after he served his second, year-long prison sentence over his anti-regime lyrics, which were described as “undermining state authority.”
In February 2012, 18-year old Walid Bahomane was charged with “defaming Morocco’s sacred values” after he posted a caricature of Mohammed VI on Facebook. Even though he did not create the illustration, Bahomane was convicted and sentenced to one year in prison for the act of sharing the image.
In the same month, Abdessamad Hidour, an activist with the 20 February Movement faced similar charges after a video of him criticising Mohammed VI was uploaded on Youtube. In the video, he likened Mohammed VI’s reign to colonialism and railed against his corrupt practices, landing him a three-year prison sentence.
These are only a few cases out of many that have drawn widespread attention over the nature of the charges as well as the expedited trials that landed all those charged in jail.
Morocco’s latest constitution supposedly grants the right to freedom of expression, but it still leaves room for repression.
The king stacked the constitutional reform deck by appointing the committee to undertake the work. The reforms introduced some liberalisation, but did not address demands for democratisation of the system. It’s an old trick dating to the 1960s when Morocco’s first constitution was drafted following its independence from France.
The latest version of the constitution incorporates human rights language and places greater attention on the legal protection of free speech, such as the following:
- Article 10 grants the opposition the “freedom of opinion, expression, and of assembly.”
- Article 25 states that “The freedoms of thought, of opinion and of expression under all their forms are guaranteed.”
- Article 28 addresses the press, “The freedom of the press is guaranteed and may not be limited by any form of prior censure.”
Out of context, these articles stand as testaments for what regime supporters describe as “landmark reforms.” However in scrutiny and in practice, these articles have proved to be futile. In Article 28, for example, immediately after stipulating the guarantee of freedom of the press, there is a caveat that leaves this article open to interpretation: “All have the right to express and to disseminate freely and within the sole limits expressly provided by the law, information, ideas, and opinion.” Immediately, “freedom of the press” is limited to a legal framework dictated by the regime and this interpretation has come into play in various recent trials where freedom of speech and press has been threatened, especially in instances when the monarchy has been the target of criticism.
The regime’s response to free speech cases following constitutional reform is swift and relatively consistent, indicating no clear break from its past policies. Despite these violations of freedom of expression, Moroccans continue to express their dissent in multiple media, from online publications to protests on the streets, indicating that the regime’s alleged “path toward reforming” is long and winding.
Samia Errazzouki is a Moroccan-American writer and co-editor of Jadaliyya’s Maghreb Page.